Controls on practice
The nursing regulations set out the restricted activities nurses are authorized to perform based on their designation. However, the reality is that nurses do not perform all these activities due to controls on their practice.
There are four controls on nursing practice limiting activities nurses can perform. Each level narrows nurses' scope of practice. Read more about the controls on practice.
Key concepts
Many of the terms and concepts used in the scope of practice standards have specific legislative meanings, which can differ from terms in everyday use.
- Authorized health professional
Authorized health professional is a health professional listed in the nursing regulations who can give an order for certain restricted activities. For example, a nurse may act on an order from a physician (an authorized professional), but not from a massage therapist (a non-listed professional). Each nursing designation has its own list of authorized health professionals.
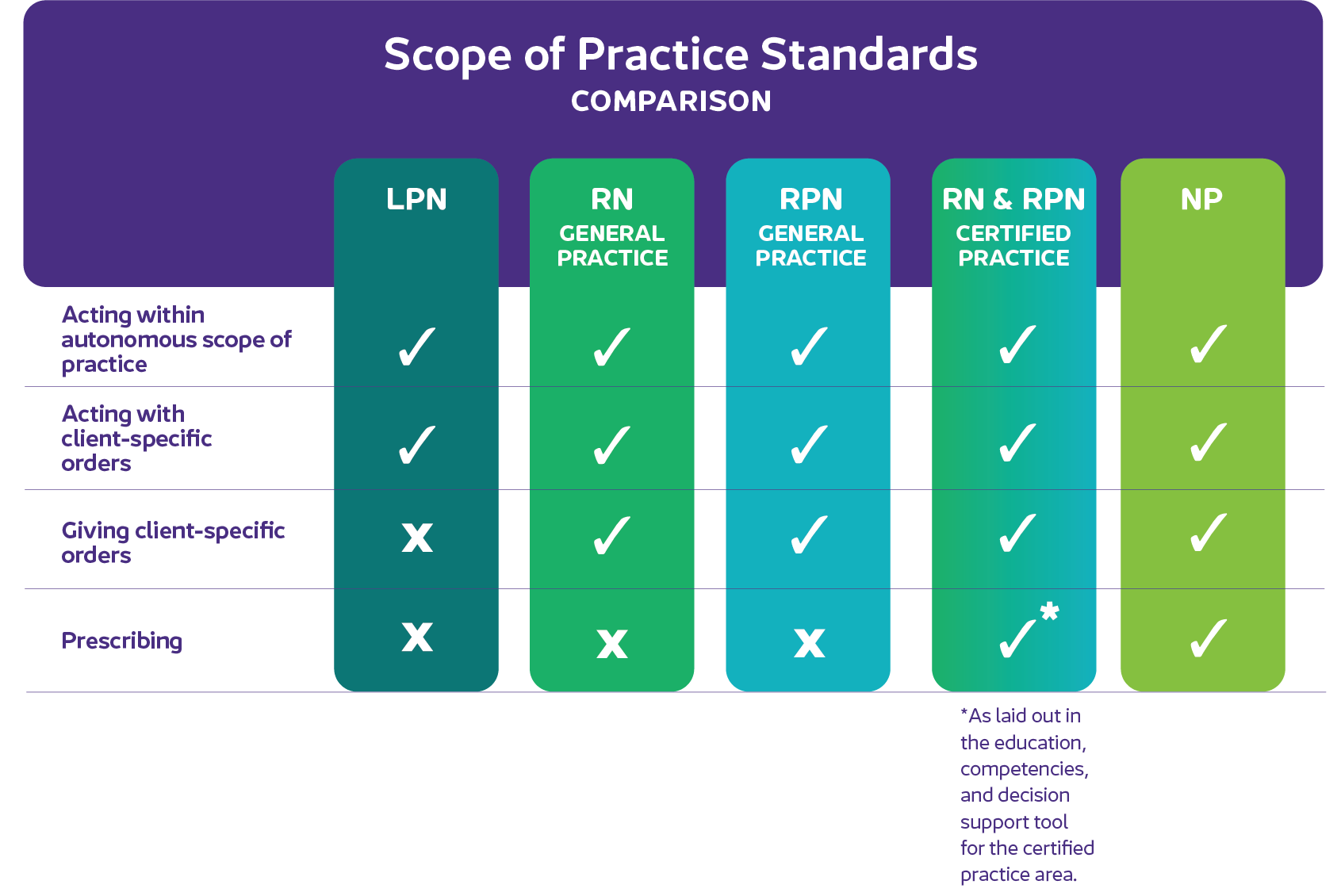
- Autonomous scope of practice
Autonomous scope of practice refers to the activities and responsibilities that a nurse is educated, competent, and authorized to perform
autonomously, without direct supervision or direction from a physician or other health-care professional. Nurses acting within their autonomous scope assume accountability and responsibility for:
Making decisions about client care, and
Performing activities that are within their autonomous scope of practice (includes activities that are not restricted and Section 6 restricted activities).
Autonomous scope of practice does not include any activities, care, or services excluded under BCCNM standards, limits, and conditions, and controls on practice.
- Client-specific order
A client-specific order, often just called an 'order', is when a regulated health professional authorizes/instructs a nurse to perform an activity for a specific client. A client-specific order can include non-restricted or restricted activities. For an order to be valid and safe, it must be documented, detailed, and signed.
- Competence
Competence is the integration and application of current knowledge, skills, attitudes, and judgment required to perform safely, ethically, and appropriately within an individual's practice.
- Nursing diagnosis
Nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment about a client's mental or physical condition. Nurses diagnose conditions, not diseases or disorders, as the cause of a client's signs or symptoms. A nursing diagnosis helps determine if nursing interventions can improve or resolve the client's condition. Certified practice nurses are authorized to diagnose a limited number of diseases and disorders.
- Prescribe
Prescribe is to issue a prescription (written or electronic) for a
pharmacist to dispense a specified medication to a specific client. Prescriptions can also be issued for medical devices. BCCNM only authorizes certified practice nurses and nurse practitioners to prescribe.
- Regulated health professional
Regulated health professional is a health professional registered with a profession's regulatory body. They meet specific requirements to be registered and abide by the bylaws and standards set by their regulatory body. Not all health professions are regulated; for example, homeopaths, clinical counsellors, and health-care aides are unregulated.
- Restricted activities
Restricted activities are clinical activities that pose a risk of harm to the public and are reserved for regulated health professionals, like nurses. These include restricted activities that “do not require an order" (section 6) and restricted activities that “require an order" (section 7).
- Scope of practice
Nursing scope of practice defines the range of duties and responsibilities that a nurse is educated, competent, and legally authorized to perform. It is shaped by nursing education, clinical experience, regulatory standards set by BCCNM, and provincial and federal laws.